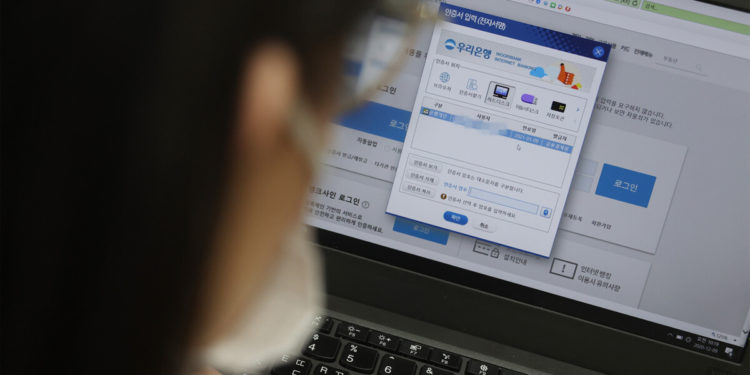
South Korea announced on Wednesday that it would introduce a more user-friendly verification system service to replace the existing official key certification system currently used by the public.
The public online identification system singularly controlled the security platform for online transactions in the country since 1999. The public key certificates would lose their official status, which would open a new market for private digital certificate providers starting Thursday.
Users could still keep their current online certificates until they become expired or choose alternative certificates issued by private firms.
The public online key certification system has nearly 46 million subscribers since its introduction in 1999 as an authentication service for government websites. However, the system required installing multiple security software, which users found difficult and complicated. It also became a problem for people residing abroad to access online services in the country.
The South Korea government promised in 2018 to phase out the system, which President Moon Jae-in included in his campaign in 2017. In May 2020, the parliament already passed a law that permits replacing the current public online identification system.
The Ministry of Science and ICT stated that the current system would no longer remain the only official verification system; other companies could already replace the system with their authentication services.
Straightforward Transformation
The transformation would expect an increase in user convenience through more straightforward procedures with biometrics, cloud services, and shorter personal identification numbers. One alternative system includes Pass, a mobile verification application from LG Uplus Corp., SK Telecom Co., and KT Corp. Pass already acquired up to 20 million registrations since April last year.
However, the government considered five candidates that would provide its digital certificate solution for the year-end tax return process starting in January. The five candidates consist of KB Kookmin Bank, NHN Payco, PASS, Kakao, and value-added service provider NICE Information & Telecommunication.
The government also intends to allow people to utilize digital certificates from private companies, like releasing copies of resident registrations. The ICT Ministry urges for an amendment of the Electronic Financial Transactions Act to create more digital certificates for the finance industry.
The Ministry also expects to develop these certificates with new technologies such as blockchain and biodata.
The Ministry said that 66.5 million registration for electronic verification came from the private sector and 46.8 million from the public system as of November 2020. Additionally, the number of digital certificates issued totaled 6.64 million in the same month.
Check out other must-read articles from KoreaTechToday: